2026 Top Types of Home Solar Systems Which One Is Right for You
As home solar systems gain traction, understanding the various types available is crucial for homeowners. Industry experts predict that the home solar market will grow by 20% annually. David Green, a well-respected solar energy consultant, notes, “Choosing the right home solar system can drastically impact your energy bills and carbon footprint.”
There are several types of home solar systems, each with unique advantages and drawbacks. For instance, grid-tied systems offer efficiency and lower costs but depend on utility power. Standalone systems provide independence but require more upfront investment. The constant evolution in solar technology means options can be confusing, and many homeowners may feel overwhelmed.
Evaluating your energy needs and financial goals is essential. Some homeowners may hesitate to move forward due to unclear benefits. However, embracing home solar can lead to significant long-term savings. Engaging with professionals in the field can help clarify choices and align them with personal objectives to create a sustainable future.

Types of Home Solar Systems: An Overview of Options Available in 2026
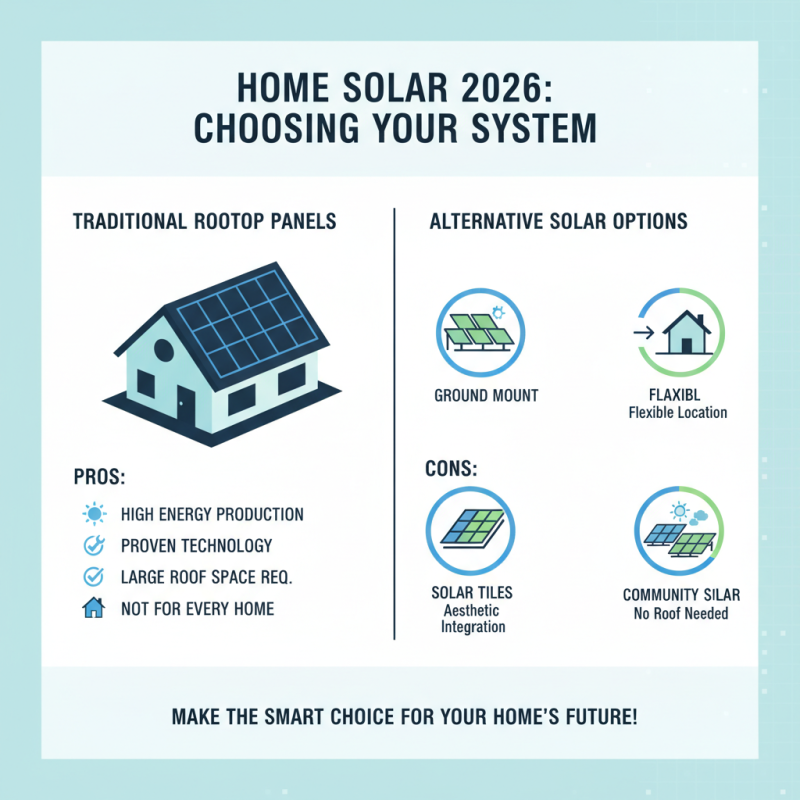
In 2026, choosing the right home solar system has become essential. Various options are available to homeowners, each with unique benefits. Traditional rooftop solar panels remain popular. These systems can generate significant electricity but also require adequate roof space. Not every home has this. It can be an issue for some families.
Another option gaining traction is solar shingles. They integrate seamlessly with your roof, providing an aesthetic appeal. However, these tend to cost more upfront and may not be as efficient as conventional panels. Homeowners must weigh these factors before making a decision.
Battery storage systems are also worth considering. They allow you to store excess energy for later use. This can be particularly beneficial during power outages. Yet, battery systems come with maintenance requirements and varying lifespans. Carefully evaluating your needs and budget is crucial.
Understanding Grid-Tied Solar Systems: Benefits and Considerations
Grid-tied solar systems are gaining popularity. They connect directly to the utility grid. This allows homeowners to use solar energy and grid energy seamlessly. One major benefit is reducing electricity bills. When the sun shines, your system generates power. Any excess goes back to the grid. You may even earn credits for this energy.
There are some considerations. First, these systems do not work during a power outage. When the grid goes down, so does your solar system. This can be a significant drawback if you live in an area with frequent outages. Maintenance can also be tricky. Keeping panels clean and in good shape is essential.
Tip: Assess your energy needs before investing in solar. Consider how much power you consume daily. It helps to match the solar output with your monthly electricity usage.
Another tip is to understand local regulations. Different areas have different rules for installation and incentives. Researching these aspects can save time and money. It's crucial to plan carefully. Home solar systems can be a big investment.
Exploring Off-Grid Solar Systems: Ideal Scenarios and Cost Analysis
Off-grid solar systems offer a unique solution for individuals seeking energy independence. These systems are particularly beneficial in remote areas where traditional electricity is unavailable. They provide power for homes, cabins, or even RVs. The initial investment can be significant, sometimes exceeding $15,000, but many find it worthwhile in the long run.
In ideal scenarios, off-grid systems excel. They allow users to produce their own energy, reducing reliance on utility companies. During outages, these systems provide a stable power source. However, potential downsides exist. Maintenance can be challenging, and battery replacement can be costly. It's essential to consider your energy usage patterns to ensure sufficient power generation year-round.
Cost analysis is crucial when exploring these systems. While off-grid solutions may seem expensive upfront, savings on monthly bills can add up. Additionally, tax incentives can help offset initial costs. Still, careful planning is necessary. One must evaluate whether the investment aligns with their long-term needs and goals. Balancing efficiency and affordability requires thoughtful reflection and research.
2026 Top Types of Home Solar Systems Which One Is Right for You - Exploring Off-Grid Solar Systems: Ideal Scenarios and Cost Analysis
| System Type | Ideal Scenario | Average Cost ($) | Battery Storage | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grid-Tied Solar System | Urban settings with grid access | $15,000 | No | Lower initial cost, no battery maintenance | Dependency on grid, no power during outages |
| Off-Grid Solar System | Remote areas without grid access | $25,000 | Yes | Energy independence, reliable in isolated areas | Higher upfront cost, battery replacement needed |
| Hybrid Solar System | Suburban areas with partial grid access | $20,000 | Yes | Flexibility to switch between grid and solar, better backup | More complex system, potential for higher maintenance |
| Community Solar Projects | Residents unable to install personal systems | Varies | No | Shared investment, lower individual costs | Less control over energy source, shared benefits |
Hybrid Solar Systems: Balancing Efficiency and Energy Independence
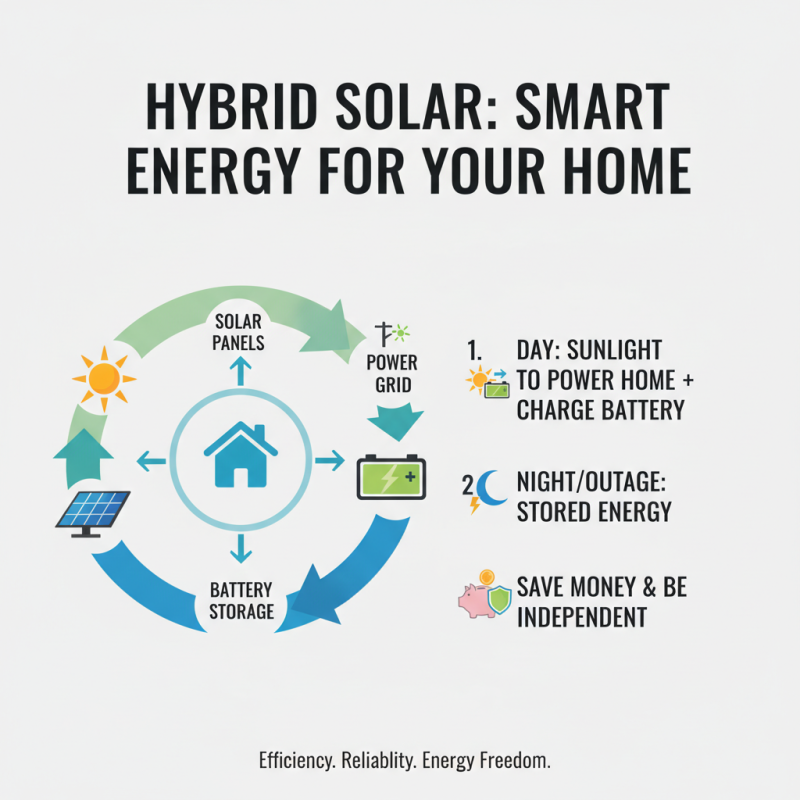
Hybrid solar systems offer a unique blend of efficiency and energy independence. They combine traditional solar panels with battery storage. This means you can harness sunlight during the day and store excess energy for later use. Imagine having power when the sun isn't shining. It can be comforting during power outages or cloudy days.
However, the installation costs can be a concern. Homeowners may face high upfront expenses. While the savings on energy bills can be significant, it takes time to see a return on investment. Many people struggle with the decision: is it worth it? Sometimes, the technology feels overwhelming. Selecting the right components can also add to the confusion.
An ongoing challenge is ensuring that your system meets your energy needs. It’s crucial to assess your household’s usage patterns. Some may find their needs shift over time. Families grow, or work-from-home scenarios change energy consumption. It’s worth reflecting on how your habits impact the efficiency of a hybrid solar setup.
Selecting the Right Solar System: Factors Influencing Your Decision in 2026
When choosing a solar system in 2026, several factors come into play. Your energy needs are paramount. Consider how much electricity you consume. Do you have electric vehicles or high energy appliances? These details will guide your selection. System size is important too. A larger system might be necessary for big households. Conversely, smaller homes may thrive on compact solutions.
Cost is another essential element. Solar panels can be a significant upfront investment. However, long-term savings on electricity are often worth it. Remember, not all systems offer the same efficiency. Some may perform poorly under certain weather conditions. Research and seek advice.
You might want to think about installation and maintenance. Not every system is easy to install. Some may require advanced setups that complicate things. Plus, ongoing maintenance is crucial. Ignored systems can fall into disrepair. Make sure you weigh the pros and cons carefully. Each decision could impact your energy future drastically.
